

 |
 |
Google has released the Flexbox which can be used for building flexible
layouts using FlexboxLayout, it can be interpreted
as an advanced LinearLayout because both layouts align their child views sequentially.There are several advantages of using FlexBox Layout
which we will see in this tutorial.
FlexboxLayout is a library project which brings the similar capabilities of
CSS Flexible Box Layout Module to Android. This means that if the width of the device changes either due to rotation or when user
is using tablets instead of stretching the elements to full width it will allow more elements in a single row.
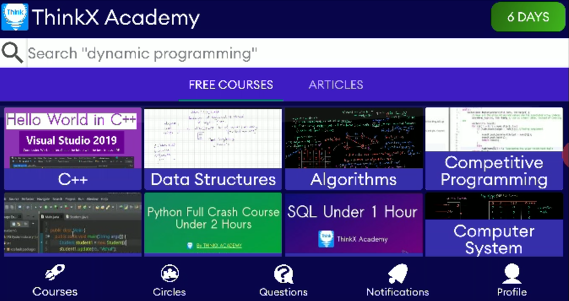
Observe two columns in a row in RecyclerView :

After rotation/device width change recyclerView has more items else two items will be stretched:
Add the following dependency to your build.gradle file: dependencies { compile 'com.google.android:flexbox:0.3.0-alpha3' }
Inside MainActivity.java :
recyclerView = view.findViewById(R.id.courses); recyclerView.setHasFixedSize(true); recyclerViewlayoutManager = new LinearLayoutManager(getActivity()); //Using FlexBox FlexboxLayoutManager layoutManager = new FlexboxLayoutManager(); layoutManager.setFlexWrap(FlexWrap.WRAP); layoutManager.setFlexDirection(FlexDirection.ROW); layoutManager.setAlignItems(AlignItems.STRETCH); layoutManager.setJustifyContent(JustifyContent.CENTER); recyclerView.setLayoutManager(layoutManager);
There are no changes in the List and RecyclerAdapter you have created inside recyclerview !!
Github Link for Google FlexBox Repository